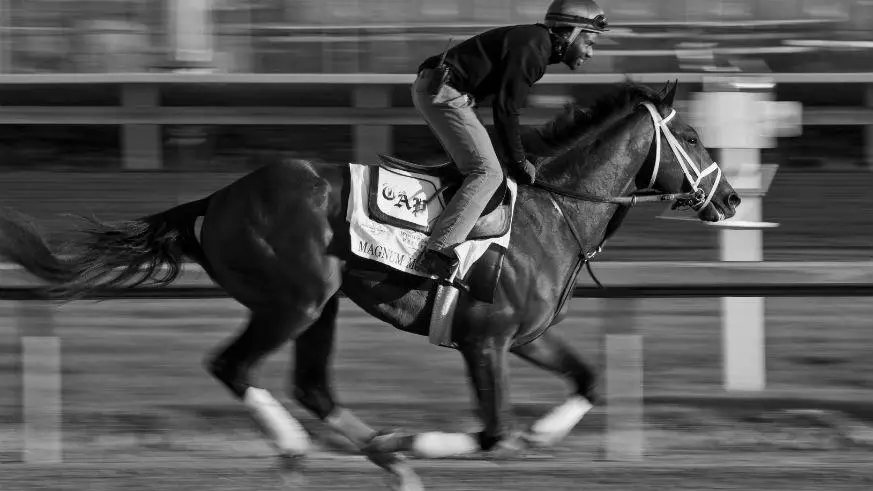
Horses are prey animals, and their ability to run has been their main evolutionary advantage over other animals. It has kept them alive for hundreds of years and made speed a high priority in breeding wild breeds. The faster a horse runs, the more likely it will survive and produce a healthy foal. Read on for more information. We are not discussing the actual time a horse can run a mile, but the maximum speed it can reach during a gallop.
Factors that affect a horse’s speed
Many factors determine a horse’s speed when running a mile. Age is a factor, because older horses tend to have more joint issues, and they put more stress on their ligaments and muscles. Another factor is breed, as different types of horses have different qualities and can be more or less fast. Draft horses, for example, are heavier and are often used for pulling heavy loads. They have low speeds, and have less endurance than racehorses.
Muscle fiber composition plays a significant role in a horse’s speed. The composition of muscle fibers is very different among different breeds of horses. Those with more fast-twitch muscle fibers may have faster top speeds, but may be better suited to long-distance competitions. In contrast, those with more slow-twitch muscle fibers may excel in shorter races.
The length of a horse’s leg is one of the most important factors in its speed. A horse’s leg length is a key factor in the distance a horse can cover in a mile. Long legs make it difficult to bring a horse forward quickly, while short legs make them faster. The distance a horse can cover in a mile depends on many factors, including the terrain. A flat surface will increase speed, whereas uneven terrain will limit it.
Another factor that affects a horse’s speed is its breed. Thoroughbred horses are the fastest breeds, and were developed by using the best breeding techniques for centuries. While a horse that runs slower than a horse with a similar breed can be a better choice for racing, a poorly bred stallion can have a difficult time reaching its maximum speed.
Besides the type of gait, age is also a factor. While a horse’s speed is largely determined by the type of gait it uses, the type of training it has received and its training also have a big impact. For example, the average speed of a thoroughbred horse is 48 miles per hour. On the other hand, a Quarter horse can reach 55 miles per hour or 88 kilometers per hour.
Lastly, a poorly maintained track can also have an impact on a horse’s speed. Poorly maintained tracks cause the horse’s hind legs to sink, which makes strides more challenging and reduces a horse’s maximum speed. While genetics are unavoidable, the horse’s conditioning and ability to perform well are factors that an owner can control. The horse must be conditioned to run regularly and not be forced to the limits every day.
One of the biggest factors that affect a horse’s speed when racing a mile is the health of the animal. Many horses have large hearts, which means they can easily pump out blood during exercise. These large hearts also help the horse avoid overworking its body and gassing during an event. In short, endurance horses have the capacity to run faster than most. A horse’s health and ability are a major factor.
Distance a horse can run
There are four main types of gaits – galloping, cantering, trotting, and walking. Each of these speeds has a direct relationship with the distance a horse can travel. In general, horses are more able to cover longer distances at a walk than at a gallop. However, if you have a young horse or plan to ride it for a long distance, you should not expect it to run as fast as a galloping horse.
Horses can run between two and five miles non-stop, but it’s essential to give them time to catch their breath. A well-conditioned horse can run about two miles non-stop before reaching exhaustion, while a more fit horse can cover up to 20 miles a day. A horse can also canter up to five miles without stopping. It is important to note that a horse’s endurance may vary by breed, training, and terrain.
The distance a horse can run a mile depends on several factors, including the breed, its physical condition, and its ability to carry weight. Ultimately, the distance a horse can run depends on how well it is fed and trained. Some breeds are better suited to running distance than others. The speed at which a horse moves also influences the distance it can run. Some horses can even run up to 15 miles at trot without much stress on their bodies.
The fastest speed a horse can run a mile depends on the type of training it has received and its overall fitness. The fastest galloping horse can cover a mile in less than two minutes. However, the horse must have the necessary rest periods between high speeds to collect energy and avoid exhaustion. It can only sustain this level of speed for short periods of time depending on how well trained it is. If the horse has a good conditioning and has sufficient stamina, it will be able to cover two to three miles without stopping.
While it is possible to push horses to run a mile without stopping, it is not recommended. Rather, horses should be built up for extended travel before they can handle longer distances. For most horses, the maximum distance is about one to two miles, while some may even go up to five miles without stopping. The danger lies in running a horse for longer than it can stand, as this can be detrimental to the horse’s health.
The average horse can cover up to eight miles per hour at a trot or a canter. This can be quite a bit, and if you’re training him regularly, he may be able to canter for seven hours. Regardless of the type of training, however, remember that horses need a break and proper nutrition before they can recover from over-exertion. And just like humans, the gait and pace of the horse determine the distance a horse can cover in a mile.
Top speed a horse can reach during a gallop
A horse’s top speed during a gallop varies depending on the gait it uses. While a walk or trot may only reach four miles per hour, the canter or gallop can reach up to 20 mph. This top speed is considerably higher than the average walking speed. During a galloping event, the horse’s top speed can reach nearly 50 mph.
Although horses are faster than humans, the average speed of a zebra is 40 miles per hour. However, many breeds of horses are even faster. While zebras can reach a maximum speed of 50 miles per hour, horses can reach nearly double that speed during a gallop. Compared to people, horses also outperform humans in jumping height and speed. If you are interested in learning more about the speed of horses, read on!
It’s possible for horses to hit speeds of more than forty miles per hour during a sprint. Several breeds of horses are faster than others, with American quarter horses reaching over 50 mph during a short race. Thoroughbreds, on the other hand, can reach speeds of up to forty-five miles per hour during a gallop. In general, a horse’s speed depends on its conformation and bloodlines.
While horses can travel at full speed for approximately three kilometers, the duration of a sprint is limited. A horse’s endurance will wear out if it does this, but if it is in excellent condition, it can continue to run at full speed for up to seven hours. A horse’s top speed during a gallop may vary significantly depending on the type of exercise it is getting, its breed, and its fitness.
Although physical ability is a huge factor, motivation is also important. If a horse is not motivated to run, it will be unlikely to reach its top speed. Seabiscuit was motivated to reach his top speed, but needed a lot of motivation and encouragement before he could hit top speed. In addition to physical ability, top speed is important for endurance racing, dressage, and show jumping. The fastest horse will survive and produce more foals.
To achieve the top speed a horse can achieve during a gallop, it must be properly trained and motivated. While horses can reach speeds of 30 mph, they will not be able to maintain this speed for more than forty minutes. As a result, endurance training is vital. Besides, endurance training is essential for the health and well-being of the horse. If the horse doesn’t get regular exercise, it will never reach its maximum speed.
As with other forms of exercise, the muscles in a horse’s legs are crucial in its performance. They have different muscle fiber types. The majority of horses have a similar composition of fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscles. The difference in muscle fiber composition is what determines a horse’s top speed. If you want to learn more about how to maximize the efficiency of your training and increase your horse’s speed, you can read the information below.
If you’ve ever wondered whether a horse will bite you when you stick your hand out to be friendly, the answer is probably yes. But the best way to avoid having your hand bitten by a horse is to learn about its bite history. A horse with a biting history is unlikely to bite you on purpose unless you’re deliberately provoking it. It’s best to keep chewables away from young horses to avoid this situation.
Getting a horse to bite you if you stick your hand out to be friendly
Getting a horse to bite you is not something you should do. You should avoid provoking your horse’s aggression and always make sure your hand is kept out of its face. Horses can bite in a number of ways, from a playful gesture to an expression of aggression. It is important to understand why your horse may bite, and how to avoid it.
When you’re trying to make a friend with a horse, remember that the animal does not know that they can hurt you. You should always remember that horses don’t know they can hurt you, and a little nibble will quickly turn into a bone-crushing bite. If you want to make a friendly encounter with your horse, try to stay away from the animal for a few hours.
Often, horses like to be petted when they’re eating. Depending on the breed of horse, you can try rubbing its muzzle or scratching its neck. Hopefully, this will make the animal feel comfortable with you. For further tips, talk to a veterinary technician or equine training provider. You might learn some new tricks. In addition to a good technique, try to be mindful of the surrounding objects and keep your horse’s attention in a safe place.
The best way to prevent a horse from biting you is to stay out of the pasture for 15 seconds before approaching it. The horse may not be afraid of you at this stage, but if he sees your hand as threatening, he will probably try to distance himself. Try not to punish him, and try not to hold the thought against him. If the animal continues to behave aggressively, the horse may be trying to avoid you altogether.
Depending on the level of fear, you may have to approach the horse one step at a time. If the horse is afraid of humans, he might require extra time to get used to your touch. Try rubbing his chest first, then moving on to his flank. Continue doing this until the horse becomes comfortable with you. It will give your horse confidence and help it to learn to be friendly with humans.
Keeping chewables out of reach of young horses
Keeping chewables out of reach of your young horse is essential for the safety of both you and your equine companion. Just like young children, young horses will chew everything they can reach. This includes your arms, clothing, and even your hands! To prevent your horse from developing a taste for your clothing, make sure chewables are out of reach. Keeping chewables out of reach of young horses is an important prevention method, but it should not be your sole goal.
Identifying the underlying reason for a horse’s aggression
Often, a horse’s aggressive behavior is caused by some underlying cause. For example, a horse with a slightly bent spine was likely to react aggressively towards another animal. In more severe cases, a horse may become overly aggressive when it is unable to escape from its precarious situation. Identifying the underlying cause for a horse’s aggression is crucial to preventing a horse from becoming overly aggressive.
Horses may exhibit aggressive behavior when they feel threatened, are trying to get away from an unfamiliar person, or have experienced something previously that causes them to become aggressive. While punishment is an effective way to stop this behavior, it is far better to identify the underlying reason for a horse’s aggression. It may have an ulcer or be improperly fed. If the cause is a mental or physical problem, you may want to consider treating it before imposing a punishment.
Identifying the underlying cause of a horse’s aggression should always begin with a thorough physical examination. A horse’s aggression could be the result of a hormonal imbalance or chronic pain. In some cases, aggressive behavior may be the result of an overproduction of testosterone. For example, a mare with an ovarian tumor or crypt-orchids might be aggressive towards another horse.
Besides addressing the physical reason for the behavior, a veterinarian can also identify underlying causes of aggressive social behavior. A veterinarian can recommend treatment methods to address these issues. Rearranging a horse’s environment can reduce the amount of distress a horse experiences. It may also help to move a mare to a more private stall. And if you are not sure what’s causing your horse’s aggression, it is worth consulting a veterinarian.
In some cases, pathologic behavior may be the result of a lack of human handling or inadequate training. In such cases, the horse’s fight-or-flight instincts are triggered by the abuse. Such “wild” horses can also become overly aggressive when they become fearful of humans or other animals. It is important to note that some horses have a more positive response than others.
Preventing a horse bite with clicker training
One method of preventing a horse bite is through clicker training. A clicker is a small device that produces a loud “click” sound when pressed. Feed a treat to your horse while making the click. Repeat several times. Eventually, you can wait a few minutes before clicking the treat. You can also tie a verbal command in with clicker training. Here are the steps to using a clicker for horse training.
A clicker is a small, manipulable object that a horse recognizes as a reward. Because it’s a tangible object, horses are more likely to repeat a behavior when rewarded. If a horse has an ST behavior problem, they may develop a compulsion to lick or focus on the clicker. This compulsive behavior may continue to occur even if training the horse is no longer pleasurable.
One method for preventing a horse bite is using the clicker. This device works by allowing you to quickly reward a horse’s behavior. The clicker signals a horse’s response, which equates to a reward. The horse will soon associate the click with a reward, so the animal will automatically be rewarded whenever it wants to be around it. This is especially effective for horses that are easily aggressive.
It is important to address the underlying cause of a horse’s biting problem. Biting is a habit that develops as a result of a lack of learning the rules of the ground. You should get a veterinarian’s help if you suspect an illness or infection. After treating the underlying cause, the biting should stop. Keep the vet’s good reputation and be on the lookout for other symptoms, which could be caused by the biting.
During the initial phase of training, your horse must understand what you expect. If he or she does not understand you, they might pull their nose away and begin to bite in a biting action. If you don’t teach him or her that he should stop biting, it will only make the situation worse. You need to be consistent and firm, but not overbearing! Remember, horses are small, fast and have powerful jaws. A biting horse can be deadly, so don’t let him or her get away with it.